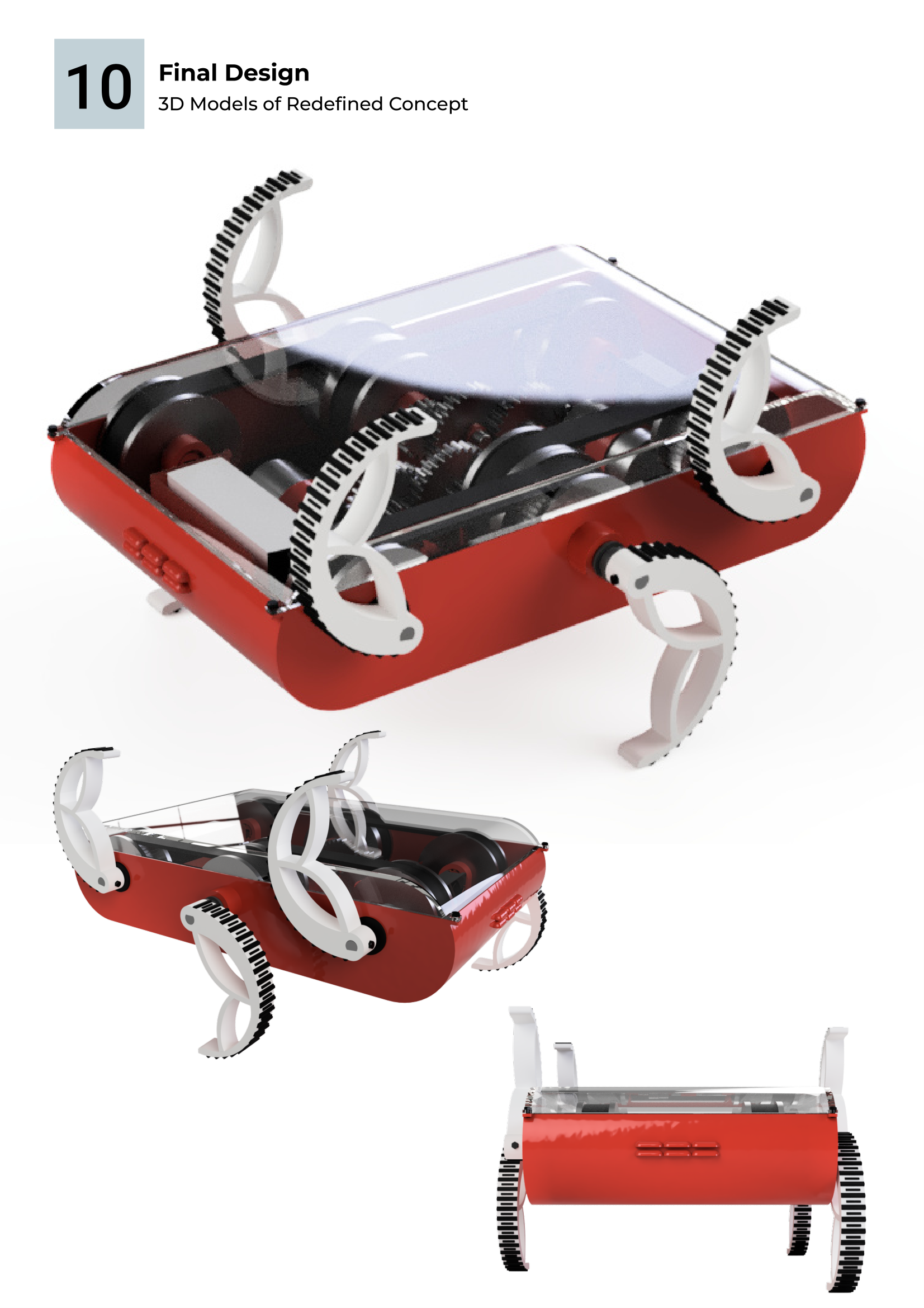
RHex imitates the movement of insects and small animals to navigate challenging terrain. Its six legs and its simple control system mimics neutral circuits found in insects. RHex is adaptable and ideal for search and rescue, reconnaissance, and environmental monitoring, and could pave the way for more efficient robotic systems in the future.
A project for Physical Computing
2022
"A Hexapod Robot is a 6-axis, parallel-kinematics machine often used for automated precision positioning and alignment of parts and components ranging from miniature optics to large panels."
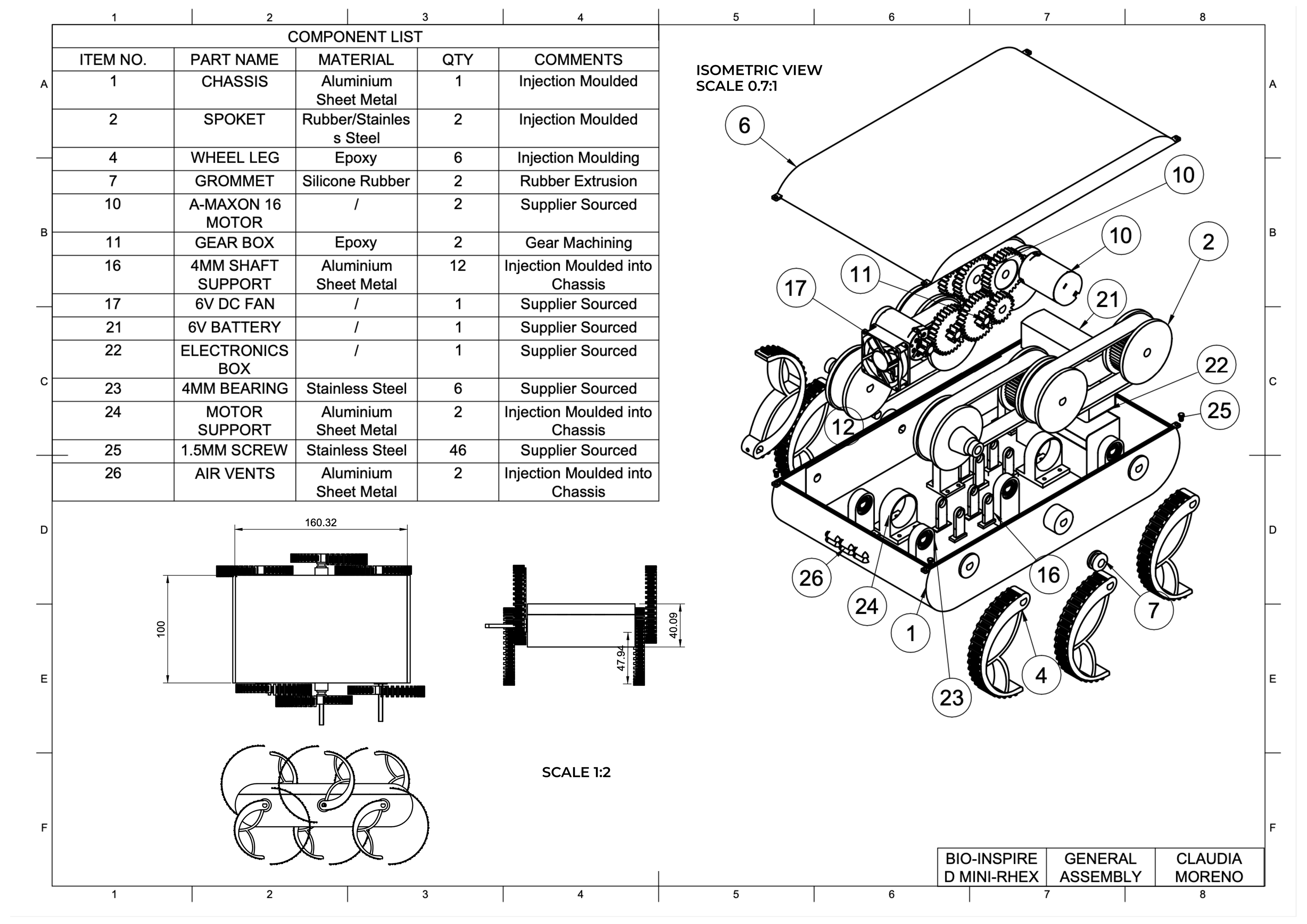
Clear lid design allows for easy maintenance if the robot
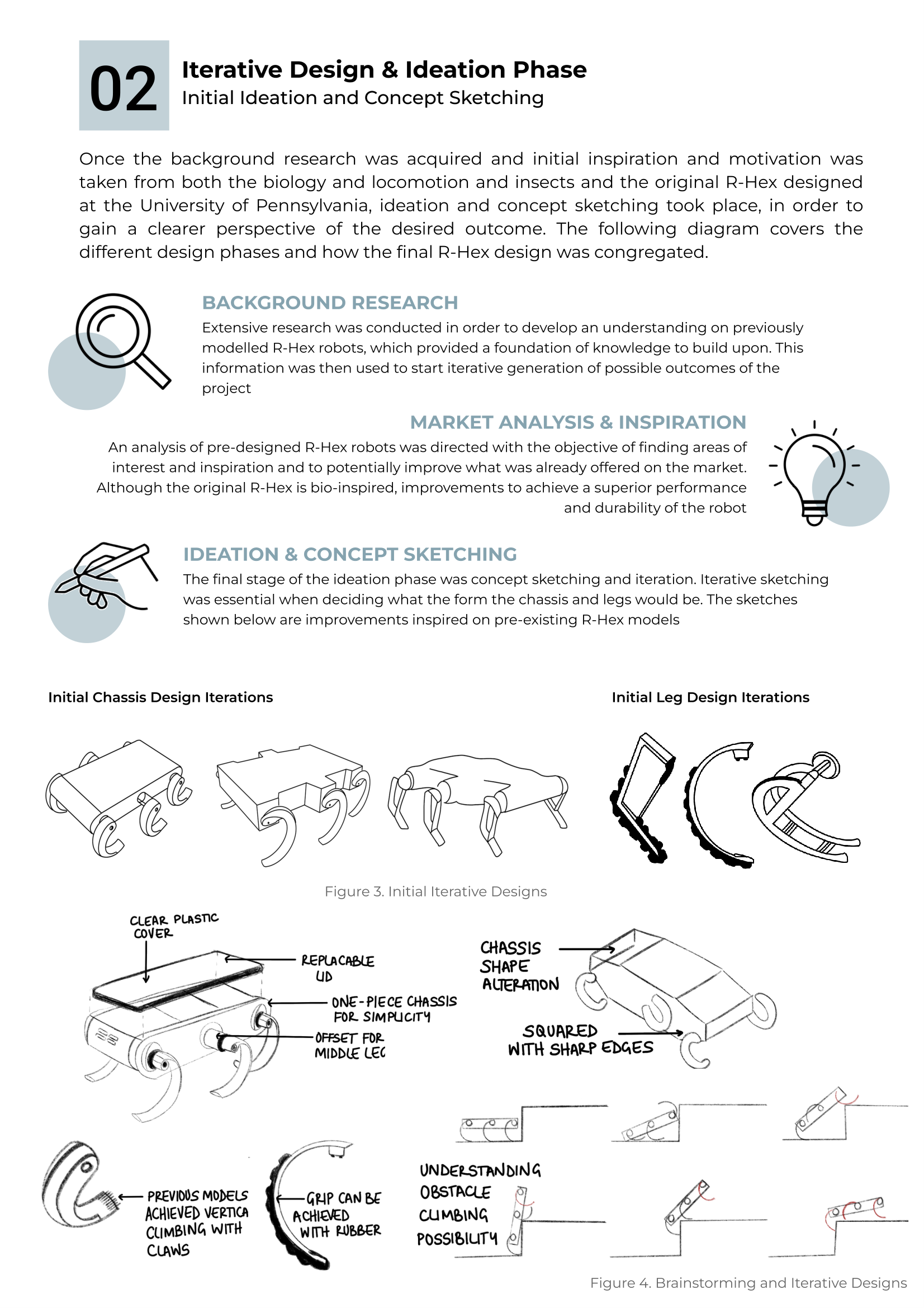
Areas of Inspiration and Ideation Phase
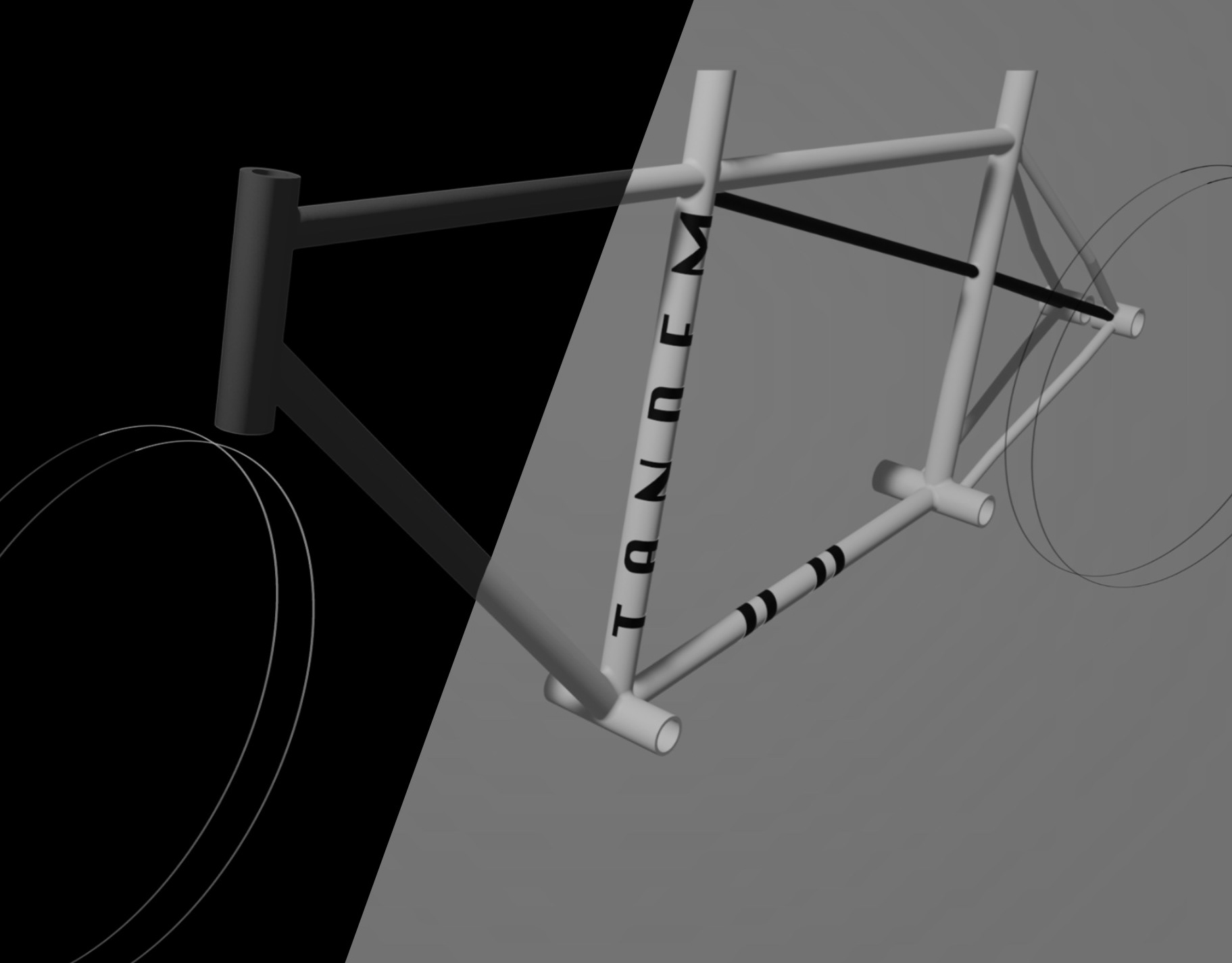
First developed in the early 2000s by a team led by Dr. Daniel E. Koditschek, a professor at the University of Pennsylvania.
This version of the Robotic Hexapod was inspired by the biology and locomotion of insects, specifically their hexapodal structure and the way they move. However, the main objective was to develop a robot that could manoeuvre over difficult terrains like insects do
First model developed by the University of Pennsylvania in the early 2000s
A suitable motor was selected after performing angular velocity and torque calculations. The total performance time of the robot is of 1.84 hours
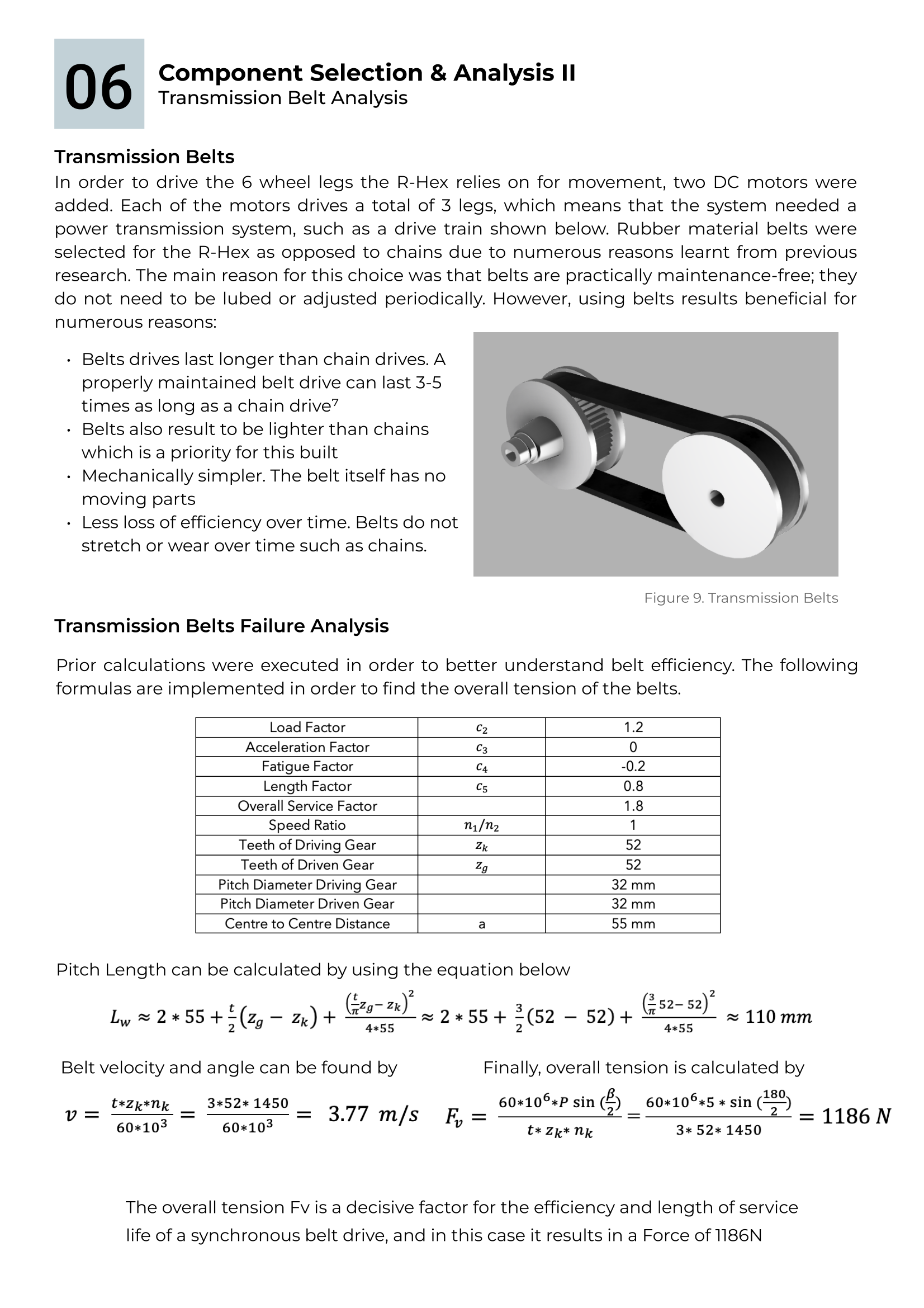
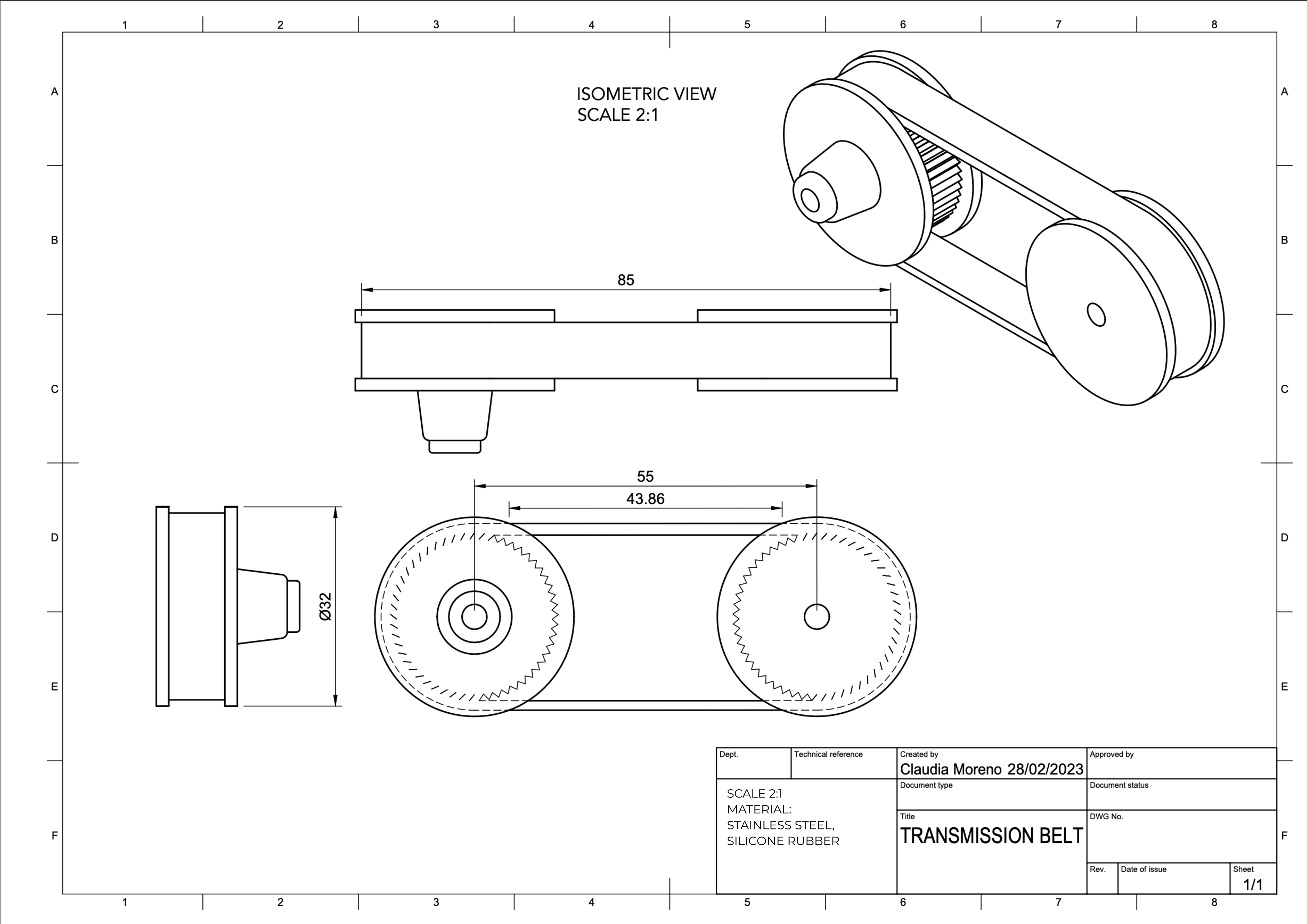
A gearbox and transmission belts were then designed in order to achieve high gear ratios
Mechanical Design & Range Calculations
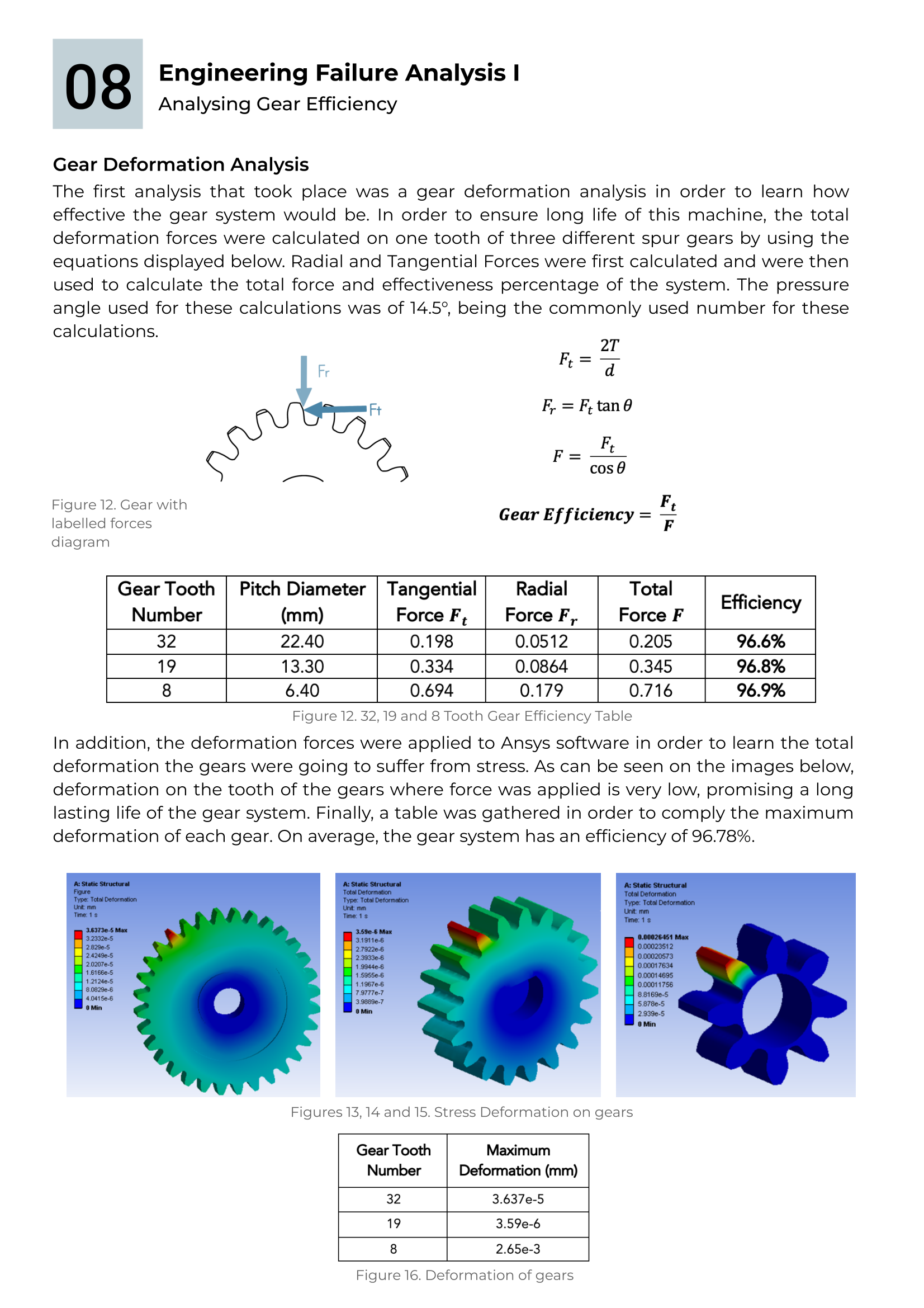
Engineering Analysis
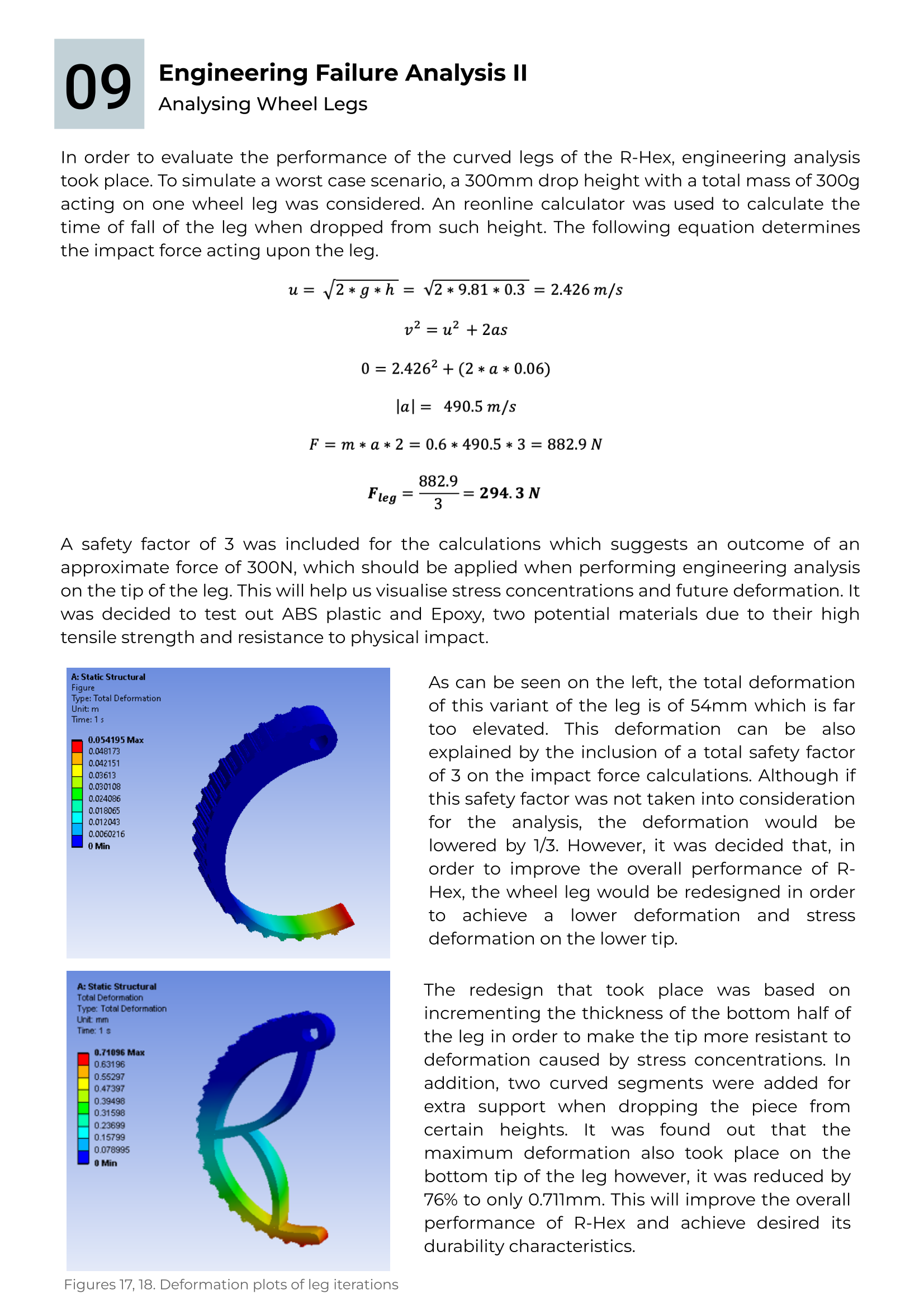
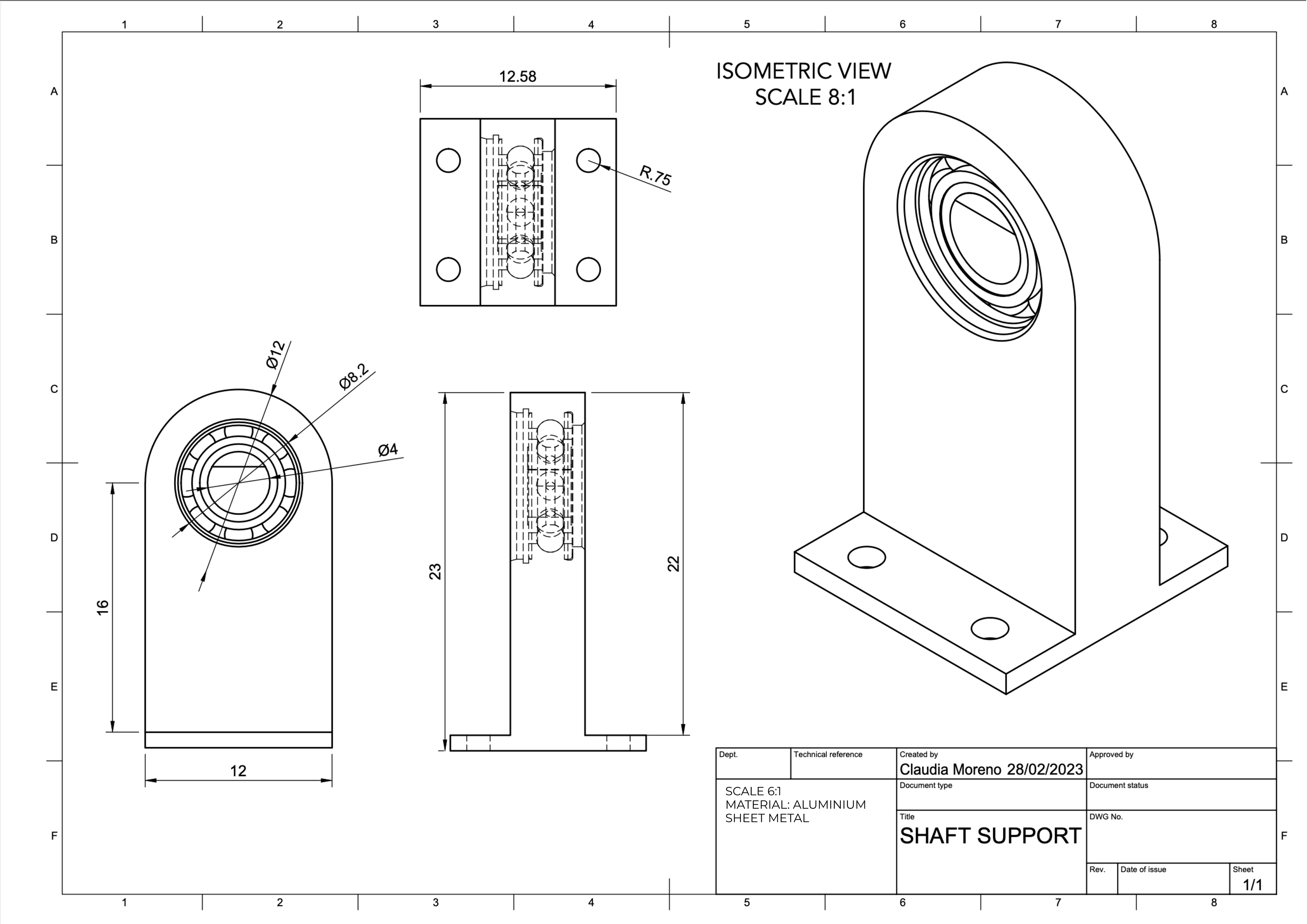
Gears were analysed in order to calculate their efficiency. Finite Element Analysis was then implemented to calculate the total deformation of the gears when applying loads. This was also executed for the legs, a very important element of the robot to maintain its position and to perform any type of movement
Final Design Features
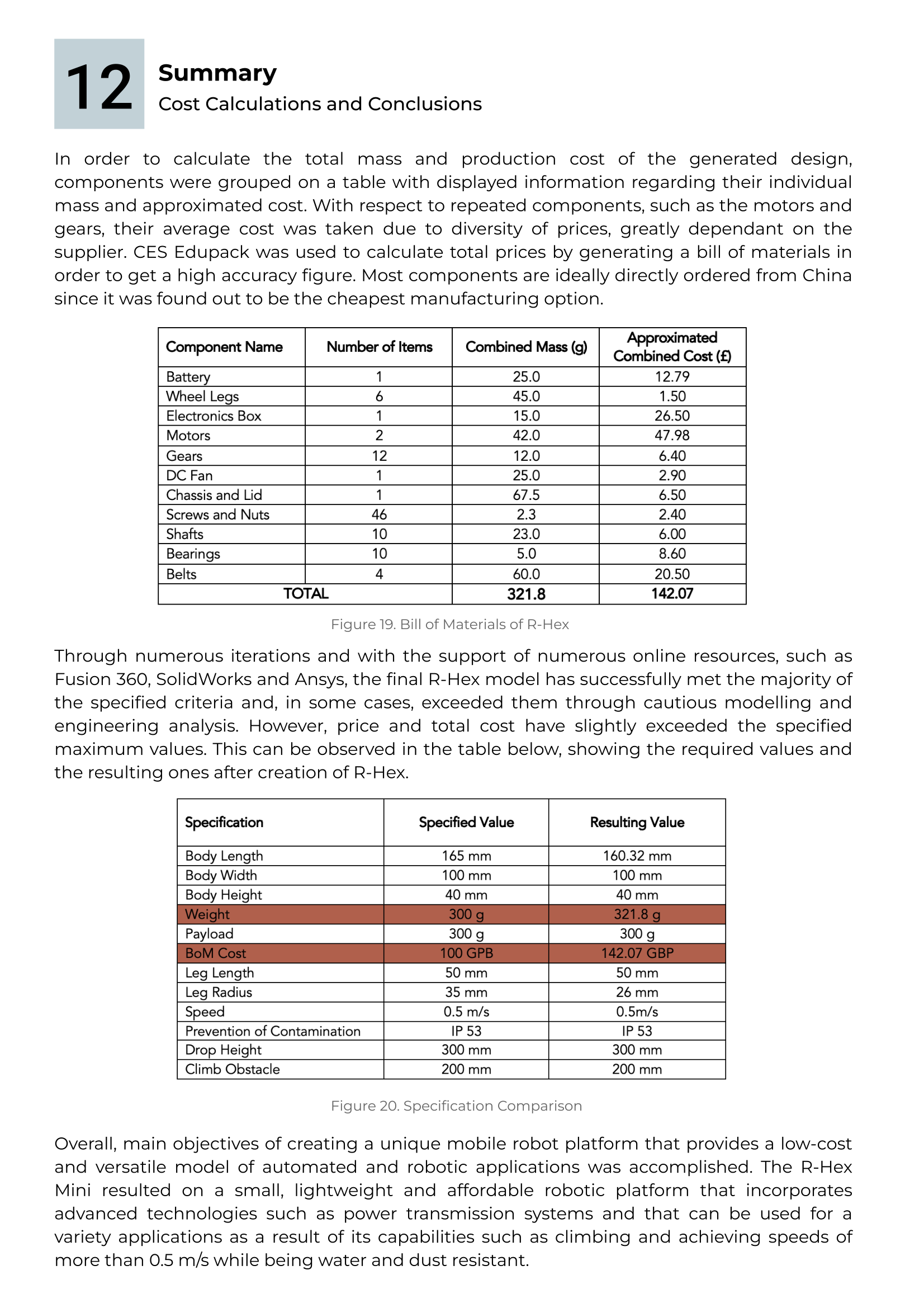
Project Documentation